Resum
Purpose: The objective was to evaluate compliance with current quality indicators of care and analyze their influence on satisfaction with patient-perceived healthcare.
Method: All HIV patients attended in a Spanish hospital between 2011 and 2017 were included for compliance with HIV quality indicators proposed by GeSIDA (Spanish AIDS Study Group).To assess patient satisfaction, the SUCE (User Satisfaction of External Consultations) questionnaire was given between February and November 2017 to those who signed the informed consent. This questionnaire was specifically designed and validated to understand the satisfaction of patients at outpatient clinics hospital. It consists of 12 items with a response scale of 1 (worst rating) to 10 (best). Through ROC curves, 6.3 was selected as value to discriminate satisfied/unsatisfied patients.
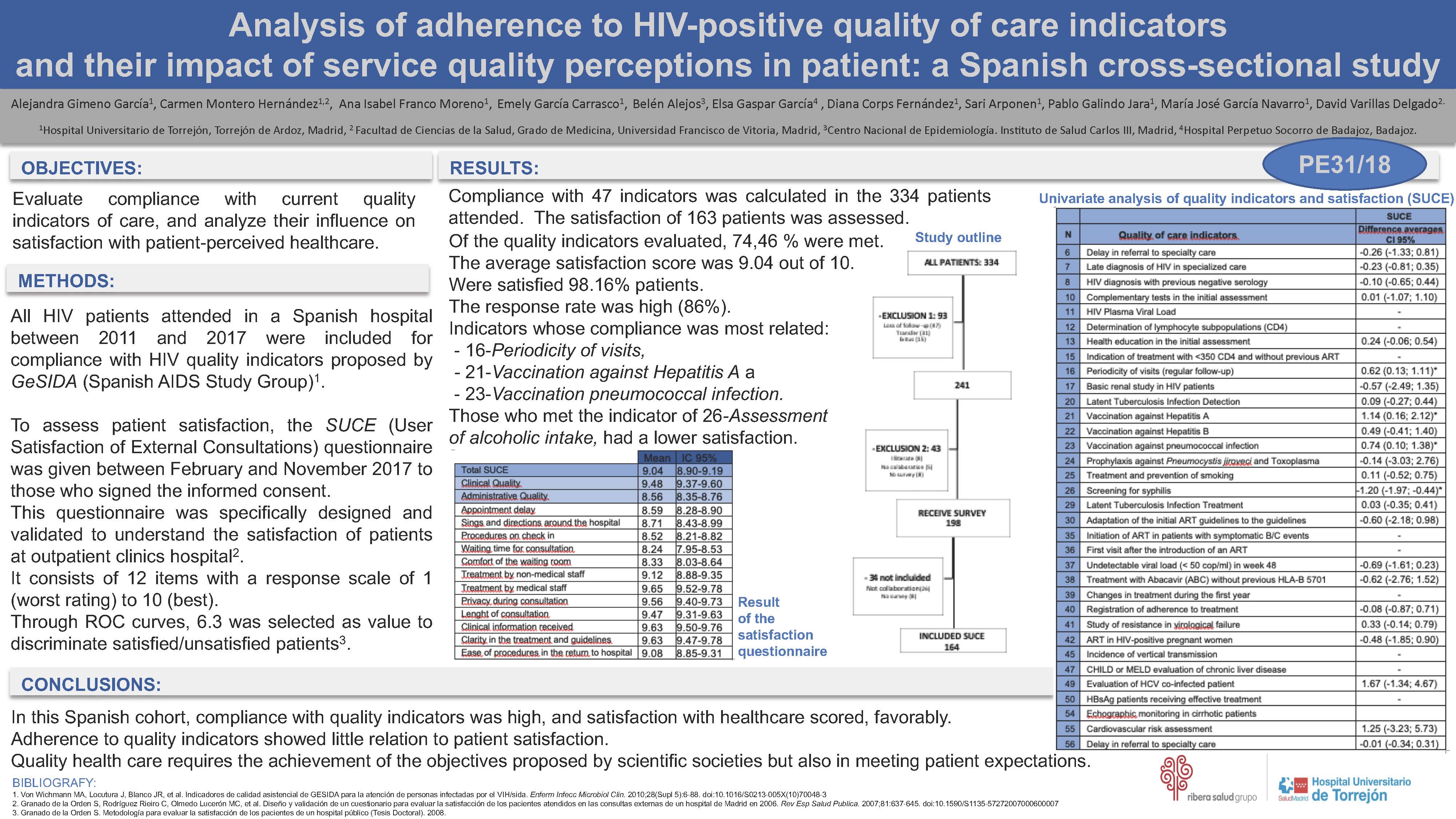
Results: Compliance with 47 indicators was calculated in the 334 patients attended. The satisfaction of 163 patients was assessed: 93 were excluded for loss of follow-up, transfer or decease, 43 for illiteracy or declined to participate. Of the 198 surveys delivered, 26 were not returned, 8 were delivered unanswered and 6 were invalid.74.46% of the quality indicators evaluated were met. The average satisfaction score was 9.04 out of 10 (95%CI:8.90-9.20). 98.16% patients were satisfied. The response rate was high (86%).
The indicators whose compliance was most related were 16-Periodicity of visits [difference of averages CI95%:0.62 (0.13-1.11)], 21-Vaccination against Hepatitis A [difference of averages CI95%:1.14(0.16-2.12)] and 23-Vaccination pneumococcal infection [difference of averages CI95%:0.74(0.10-1.38)]. Those who met the indicator of 26-Assessment of alcoholic intake had a lower satisfaction [difference of averages 95%CI: -1.20(-1.97-0.44)].
Conclusion: In this Spanish cohort, compliance with quality indicators was high, and satisfaction with healthcare scored, favorably.Adherence to quality indicators showed little relation to patient satisfaction. Quality health care requires the achievement of the health objectives proposed by scientific societies but also in meeting patient expectations.
Autoria:
GIMENO GARCÍA, Alejandra;
MONTERO HERNÁNDEZ, Carmen;
FRANCO MORENO, Ana Isabel;
GARCÍA CARRASCO, Emely;
ALEJOS FERRERAS, Belén;
GASPAR GARCÍA, Elsa;
CORPS FERNÁNDEZ, Diana;
ARPONEN, Sari;
GALINDO JARA, Pablo;
GARCÍA NAVARRO, María José;
VARILLAS DELGADO, David